A young adult presented with lingering sensitivity in her upper front tooth, almost a decade after a traumatic dental injury. Clinical and radiographic evaluations revealed severe pulp canal obliteration (PCO). Owing to the complexity and risk of conventional access, a precision-guided endodontic approach was adopted — involving CBCT integration, virtual planning, and a 3D-printed guide.
Chief Complaint
Sensitivity in the upper front tooth (tooth 11), especially on consuming cold foods.
History
- Trauma: Tooth 11 suffered trauma approximately 9 years back.
- Orthodontic Treatment: Completed fixed orthodontics with retention using Essix retainers.
- Symptoms Over Time: Progressive discoloration of 11, episodes of sensitivity.
Clinical Examination
- Discoloration of 11 noted.
- No sinus tract, swelling, or mobility.
- Non-tender on percussion.
Investigations
Preoperative IOPA: Shows canal obliteration in 11.
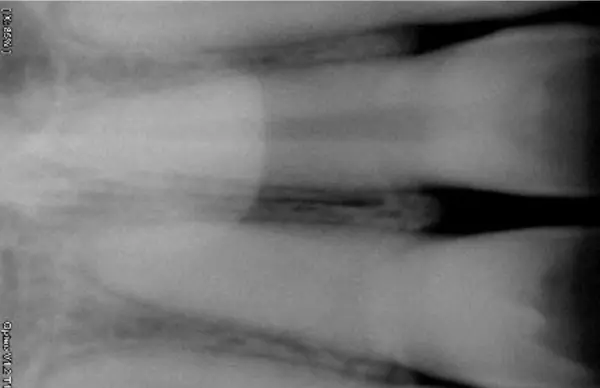
CBCT (Sectional): Revealed severe PCO in 11 without periapical changes.
Diagnosis
Pulp Canal Obliteration (PCO) in Tooth 11 secondary to previous trauma.
Treatment Plan
Due to the high risk of misdirection and perforation during conventional access, a guided endodontic protocol was opted for:
- Virtual planning using CBCT and intraoral scans
- Fabrication of a 3D-printed guide
- Targeted access through obliterated canal
Guided Endodontic Procedure – Stepwise
Step 1. Planning
- CBCT + STL merged to plan precise path
Step 2. Surgical Guide
- Guide trial & placement intraorally

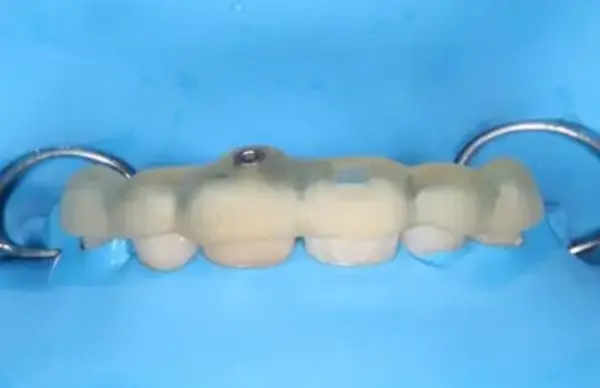
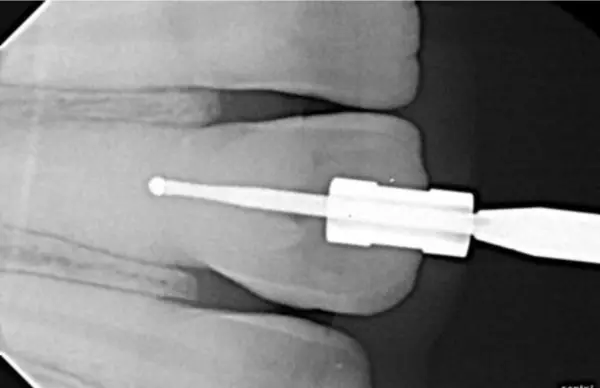
Step 3. Access Preparation
File introduced through guided path
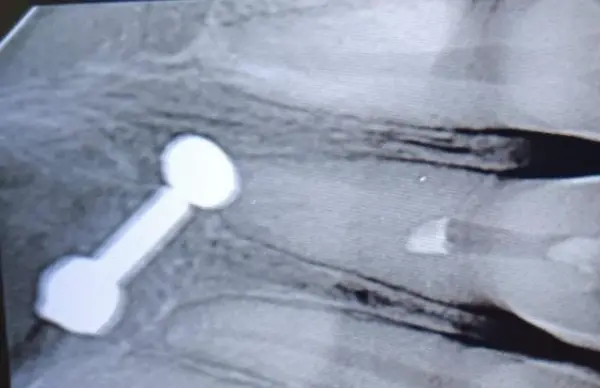
Step 4. Obturation
WL determined; obturation completed
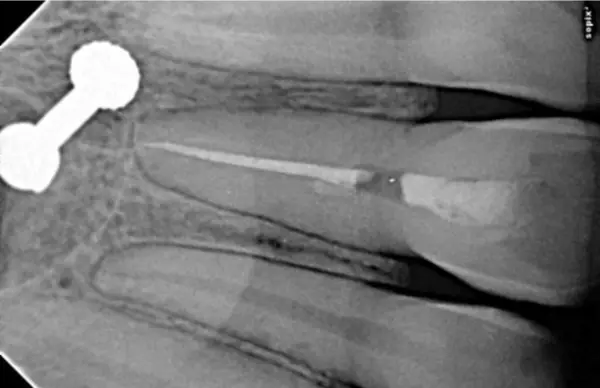
Restoration
Composite resin build-up was performed immediately post obturation.
Aesthetic options will be evaluated in future review.
Outcome
- PCO canal in 11 successfully negotiated and obturated.
- Conservative access achieved without structural compromise.
- Post-op radiograph confirmed optimal obturation.
Before–After Comparison
Before – IOPA showing obliterated canal:
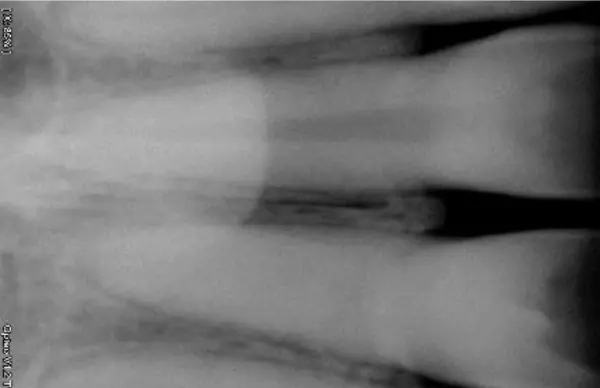
After – Well-obturated canal with intact periapical status:

Clinical Significance
Guided endodontics empowers clinicians to approach PCO cases with accuracy and safety. In this case, technology-enabled access allowed for:
- Preservation of remaining tooth structure
- Avoidance of procedural errors
- Predictable treatment of a highly calcified canal
Contributors
- Dr. Reuben – Guided Endodontic Planning and RCT
- Dr. Roshan – Orthodontic Management, Clinical Lead & Comprehensive Case Oversight (Monitoring, and interdepartmental guidance)
Conclusion:
Guided endodontics has emerged as a precise and minimally invasive technique for managing calcified root canals, especially in anterior teeth like tooth 11 following trauma. In this case, digital planning and 3D-printed guides allowed for accurate canal location and preservation of tooth structure, significantly reducing the risk of procedural errors such as perforation. The success of treatment highlights the value of incorporating advanced technologies into endodontic protocols, particularly when conventional methods are limited by extensive canal calcification.
Read also: Laser Tongue Tie
