Why This Case Stands Out
Managing precooperative toddlers poses a unique challenge — especially when multiple minor dental procedures are indicated. In this case, a calm, safe and stress-free experience was achieved through IV sedation in a 23-month-old child, ensuring high-quality treatment without emotional trauma.
Clinical Concerns
- Dental caries in 51 and 61.
- High frenal attachment compromising oral hygiene and contributing to anterior caries.
- Multiple proximal contacts and early demineralisation in upper anteriors.
- Need for preventive measures and minor corrections to avoid future caries progression.
- Patient uncooperative due to age — conventional chairside treatment not feasible.
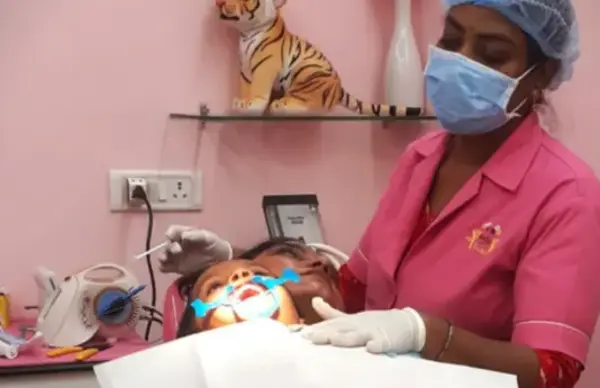
Rationale Behind IV Sedation
✅ This was nota full mouth rehab case requiring GA or hospital admission.
✅ Procedures were short, surface-level, and preventive in intent.
✅ IV sedation allowed for:
- Seamless and efficient treatment
- Immediate recovery post-procedure
- Avoiding the logistics of admission or OT scheduling
📌 Note: IV sedation is routinely used at our centre in precooperative toddlers when treatment can be completed in a single, controlled session.
✳️ “GA isn’t the only route — in select cases, IV sedation gives us the best of both: safety and speed.”
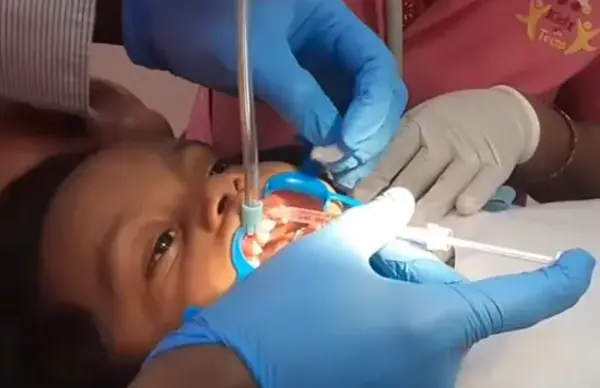
Comprehensive Care Delivered in One Sitting
| Procedure | Teeth | Description |
| Proximal Stripping | 51, 52, 61, 62 | Contact relief for preventive correction |
| Macroabrasion | 52, 62, 51, 61 | Smoothening incisal surfaces with early enamel lesions |
| Filling | 51, 61 | Conservative restoration of early caries |
| Sealants | 54, 64,74,84 | Pit and fissure sealing for caries prevention |
| Fluoride Varnish | Full mouth | Enamel remineralisation and caries control |
| Laser Frenectomy | – | For high frenal attachment affecting hygiene and contributing to DC in 51 and 61 |
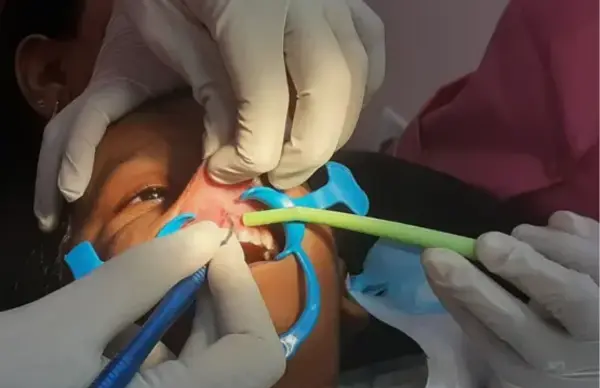
Clinical Significance
This case reinforces the use of IV sedation as a safe, controlled alternative for minor pediatric dental procedures. It’s not only less invasive than GA, but also logistically efficient and psychologically lighter for both parents and the child.
✨ IV sedation — especially in expert hands — allows pediatric dentists to deliver quality care even in challenging behavior profiles.
Conclusion
Early pediatric dental intervention under IV sedation enabled safe, effective treatment for a precooperative toddler with extensive dental needs. The approach minimized trauma, ensured full-mouth rehabilitation in one visit, and promoted long-term oral health. IV sedation proved essential in managing behavior and anxiety. This case reinforces the importance of timely, tailored care in pediatric dentistry.
